Explore Career Paths in Geospatial Analysis and Future Opportunities
As public spaces continue to evolve, careers focused on mapping and analyzing urban environments have seen a rise in relevance. Just as artists reimagine cities through vibrant street murals, professionals in geospatial analysis reshape how we understand and interact with evolving landscapes. This field blends technology, spatial science, and geographic insight to support planning, development, and decision-making across sectors. Whether tracking environmental patterns or enhancing urban infrastructure, those pursuing geospatial analysis often explore diverse roles and industry applications. Learn more about how this path is expanding.
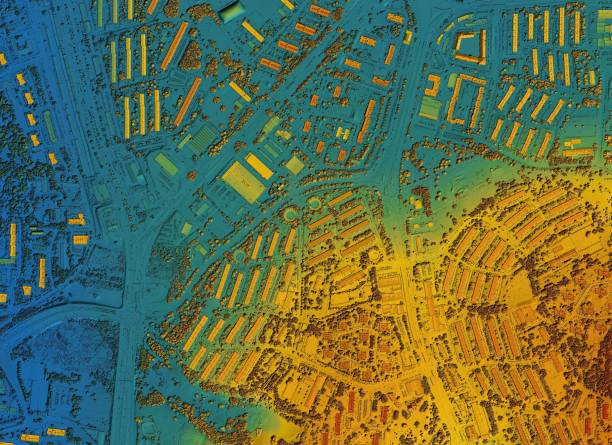
What Are Geospatial Career Opportunities Today?
Geospatial career opportunities span multiple industries and continue to expand as technology evolves. Entry-level positions typically include GIS Technicians, Mapping Technicians, and Junior GIS Analysts. These roles focus on data collection, map creation, and basic spatial analysis, providing a foundation for advancement. Many organizations, including government agencies, environmental firms, and technology companies, hire entry-level geospatial professionals [1].
The emergence of cloud-based GIS platforms has created new positions focused on web mapping and spatial data management. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence with geospatial technologies has spawned specialized roles in machine learning applied to spatial data. Fields like precision agriculture, smart city development, and emergency management increasingly rely on geospatial expertise, creating diverse career paths for those entering the industry.
How Do Urban Planning Jobs Utilize Geospatial Skills?
Urban planning jobs represent one of the most established career paths for geospatial professionals. Entry-level positions such as Planning Technicians or Assistant Planners often require GIS skills to analyze land use patterns, transportation networks, and demographic data. These professionals create zoning maps, conduct site suitability analyses, and help visualize development scenarios using geospatial tools [1].
Smart city initiatives have significantly expanded the role of geospatial analysis in urban planning. Entry-level professionals may work on projects involving traffic management systems, public transit optimization, or urban heat island analysis. The ability to create compelling visual representations of complex spatial data makes geospatial analysts particularly valuable in community engagement efforts and in communicating planning concepts to stakeholders and the public.
What Is the Average GIS Analyst Salary for Entry-Level Positions?
The GIS analyst salary range for entry-level positions varies based on location, industry, and educational background. Generally, entry-level GIS analysts can expect starting salaries between $40,000 and $55,000 annually in the United States. Those with specialized skills or advanced degrees may command higher compensation. Government positions often offer competitive benefits packages that enhance overall compensation.
Experience rapidly increases earning potential in this field. After 2-3 years of experience, many GIS analysts see significant salary growth, with mid-level positions frequently paying $60,000-$75,000. Industries such as utilities, oil and gas, and technology typically offer higher salaries compared to non-profit or some government sectors. Additionally, obtaining professional certifications like GISP (Geographic Information Systems Professional) can positively impact salary negotiations.
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
How Are Remote Sensing Careers Evolving?
Remote sensing careers have transformed dramatically with technological advancements in satellite imagery, drone technology, and sensor development. Entry-level positions include Remote Sensing Technicians, Imagery Analysts, and Drone Operators. These roles focus on acquiring, processing, and interpreting data collected from satellites, aircraft, and unmanned aerial vehicles to extract valuable insights about the Earth’s surface [1].
Environmental monitoring represents a significant growth area within remote sensing. Entry-level professionals may work on projects tracking deforestation, monitoring crop health, or assessing natural disaster impacts. The defense and intelligence sectors also employ numerous remote sensing specialists for security applications. With the commercialization of space and increasing satellite launches, opportunities continue to expand for those with skills in processing and analyzing remotely sensed data.
Which Industries Offer the Best Entry-Level Geospatial Opportunities?
Several industries stand out for offering exceptional entry-level geospatial opportunities. Technology companies like Esri, Google, and Microsoft hire GIS specialists to improve mapping products and location-based services. These positions often provide exposure to cutting-edge technology and competitive compensation packages.
Environmental consulting firms regularly employ entry-level geospatial analysts to support environmental impact assessments, habitat conservation planning, and natural resource management. The utilities sector, including electric, gas, and telecommunications companies, offers stable career paths focused on infrastructure mapping and network analysis. Government agencies at federal, state, and local levels maintain large GIS departments with structured advancement opportunities for new professionals.
| Industry | Entry-Level Position | Average Starting Salary | Growth Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Junior GIS Developer | $55,000-$65,000 | High |
| Environmental | GIS Technician | $40,000-$50,000 | Moderate |
| Local Government | Planning Assistant | $45,000-$55,000 | Moderate |
| Utilities | GIS Analyst I | $50,000-$60,000 | High |
| Transportation | Mapping Specialist | $42,000-$52,000 | Moderate |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
What Skills Should You Develop for a Successful Geospatial Career?
Developing a competitive skill set is crucial for success in geospatial careers. Proficiency in industry-standard software such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and Google Earth Engine provides a strong foundation. Programming abilities, particularly in Python, R, or JavaScript, are increasingly valuable as automation and custom tool development become more common in workflows [1].
Database management skills, especially with spatial databases like PostgreSQL/PostGIS, enhance employability significantly. Knowledge of web mapping technologies (Leaflet, MapBox, OpenLayers) opens doors to the growing field of web-based GIS applications. Beyond technical skills, effective communication abilities are essential, as geospatial professionals often need to explain complex spatial concepts to non-technical audiences. Successful professionals also cultivate project management capabilities and domain knowledge in their industry of focus, whether that’s urban planning, environmental science, or another field.
The geospatial industry continues to evolve rapidly, creating diverse and rewarding career paths for those entering the field. From urban planning to remote sensing, opportunities exist across multiple sectors, with competitive salaries and significant growth potential. By developing relevant technical skills and understanding industry applications, new professionals can position themselves for success in this dynamic field.
Sources:
- [1] https://www.coursera.org/specializations/gis




